Lecture: Interior-Point Methods (Cont.)
Stephen Boyd - Stanford
Description
Lecture Description
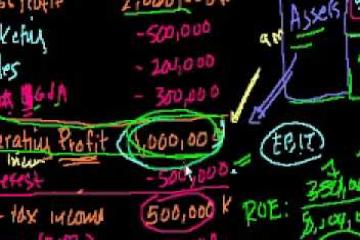
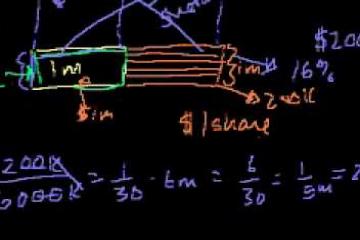
Interior-Point Methods (Cont.), Example, Barrier Method (Review), Complexity Analysis Via Self-Concordance, Total Number Of Newton Iterations, Generalized Inequalities, Logarithmic Barrier And Central Path, Barrier Method, Course Conclusion, Further Topics
Course Description
Concentrates on recognizing and solving convex optimization problems that arise in engineering.
Topics include: Convex sets, functions, and optimization problems. Basics of convex analysis. Least-squares, linear and quadratic programs, semidefinite programming, minimax, extremal volume, and other problems. Optimality conditions, duality theory, theorems of alternative, and applications. Interiorpoint methods. Applications to signal processing, control, digital and analog circuit design, computational geometry, statistics, and mechanical engineering.
Prerequisites: Good knowledge of linear algebra. Exposure to numerical computing, optimization, and application fields helpful but not required; the engineering applications will be kept basic and simple.
from course: Convex Optimization I




Comments